Writing Equations of Hyperbolas in Standard Form
Just as with ellipses, writing the equation for a hyperbola in standard form allows us to calculate the key features: its center, vertices, co-vertices, foci, asymptotes, and the lengths and positions of the transverse and conjugate axes. Conversely, an equation for a hyperbola can be found given its key features. We begin by finding standard equations for hyperbolas centered at the origin. Then we will turn our attention to finding standard equations for hyperbolas centered at some point other than the origin.
Hyperbolas Centered at the Origin
Reviewing the standard forms given for hyperbolas centered at , we see that the vertices, co-vertices, and foci are related by the equation . Note that this equation can also be rewritten as . This relationship is used to write the equation for a hyperbola when given the coordinates of its foci and vertices.How To: Given the vertices and foci of a hyperbola centered at , write its equation in standard form.
- Determine whether the transverse axis lies on the x- or y-axis.
- If the given coordinates of the vertices and foci have the form and , respectively, then the transverse axis is the x-axis. Use the standard form .
- If the given coordinates of the vertices and foci have the form and , respectively, then the transverse axis is the y-axis. Use the standard form .
- Find using the equation .
- Substitute the values for and into the standard form of the equation determined in Step 1.
Example 2: Finding the Equation of a Hyperbola Centered at (0,0) Given its Foci and Vertices
What is the standard form equation of the hyperbola that has vertices and fociSolution
The vertices and foci are on the x-axis. Thus, the equation for the hyperbola will have the form . The vertices are , so and . The foci are , so and . Solving for , we have
Finally, we substitute and into the standard form of the equation, . The equation of the hyperbola is .
 Figure 6
Figure 6Hyperbolas Not Centered at the Origin
Like the graphs for other equations, the graph of a hyperbola can be translated. If a hyperbola is translated units horizontally and units vertically, the center of the hyperbola will be . This translation results in the standard form of the equation we saw previously, with replaced by and replaced by .A General Note: Standard Forms of the Equation of a Hyperbola with Center (h, k)
The standard form of the equation of a hyperbola with center and transverse axis parallel to the x-axis is
where
- the length of the transverse axis is
- the coordinates of the vertices are
- the length of the conjugate axis is
- the coordinates of the co-vertices are
- the distance between the foci is , where
- the coordinates of the foci are
where
- the length of the transverse axis is
- the coordinates of the vertices are
- the length of the conjugate axis is
- the coordinates of the co-vertices are
- the distance between the foci is , where
- the coordinates of the foci are
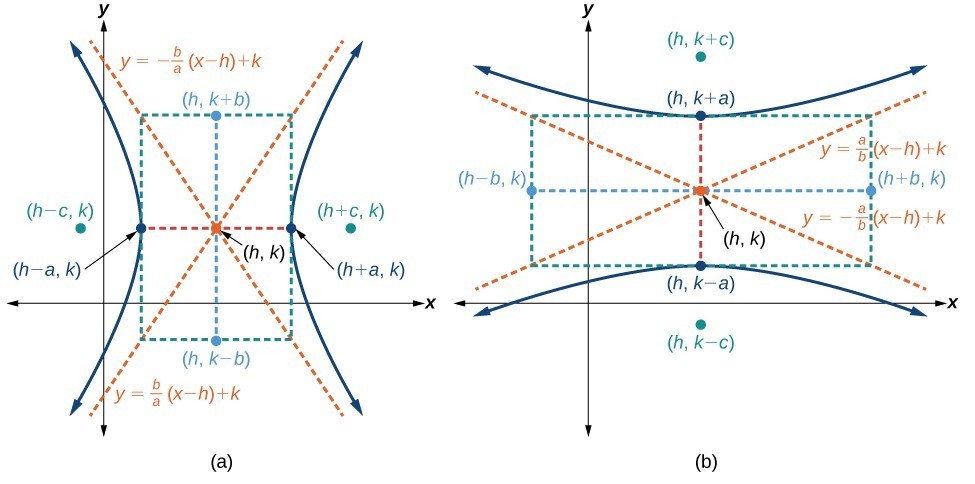 Figure 7. (a) Horizontal hyperbola with center (b) Vertical hyperbola with center
Figure 7. (a) Horizontal hyperbola with center (b) Vertical hyperbola with center How To: Given the vertices and foci of a hyperbola centered at , write its equation in standard form.
- Determine whether the transverse axis is parallel to the x- or y-axis.
- If the y-coordinates of the given vertices and foci are the same, then the transverse axis is parallel to the x-axis. Use the standard form .
- If the x-coordinates of the given vertices and foci are the same, then the transverse axis is parallel to the y-axis. Use the standard form .
- Identify the center of the hyperbola, , using the midpoint formula and the given coordinates for the vertices.
- Find by solving for the length of the transverse axis, , which is the distance between the given vertices.
- Find using and found in Step 2 along with the given coordinates for the foci.
- Solve for using the equation .
- Substitute the values for , and into the standard form of the equation determined in Step 1.
Example 3: Finding the Equation of a Hyperbola Centered at (h, k) Given its Foci and Vertices
What is the standard form equation of the hyperbola that has vertices at and and foci at andSolution
The y-coordinates of the vertices and foci are the same, so the transverse axis is parallel to the x-axis. Thus, the equation of the hyperbola will have the form
First, we identify the center, . The center is halfway between the vertices and . Applying the midpoint formula, we have
Next, we find . The length of the transverse axis, , is bounded by the vertices. So, we can find by finding the distance between the x-coordinates of the vertices.
Now we need to find . The coordinates of the foci are . So and . We can use the x-coordinate from either of these points to solve for . Using the point , and substituting ,
Next, solve for using the equation
Finally, substitute the values found for , and into the standard form of the equation.
